Tsinghua University
Johns Hopkins University
Tsinghua University, IDEA
University of Chicago
Tsinghua University
IDEA
IDEA
HKU
Johns Hopkins University
IDEA
Tsinghua University
CVPR 2025
*Equal Contribution, †Corresponding Author

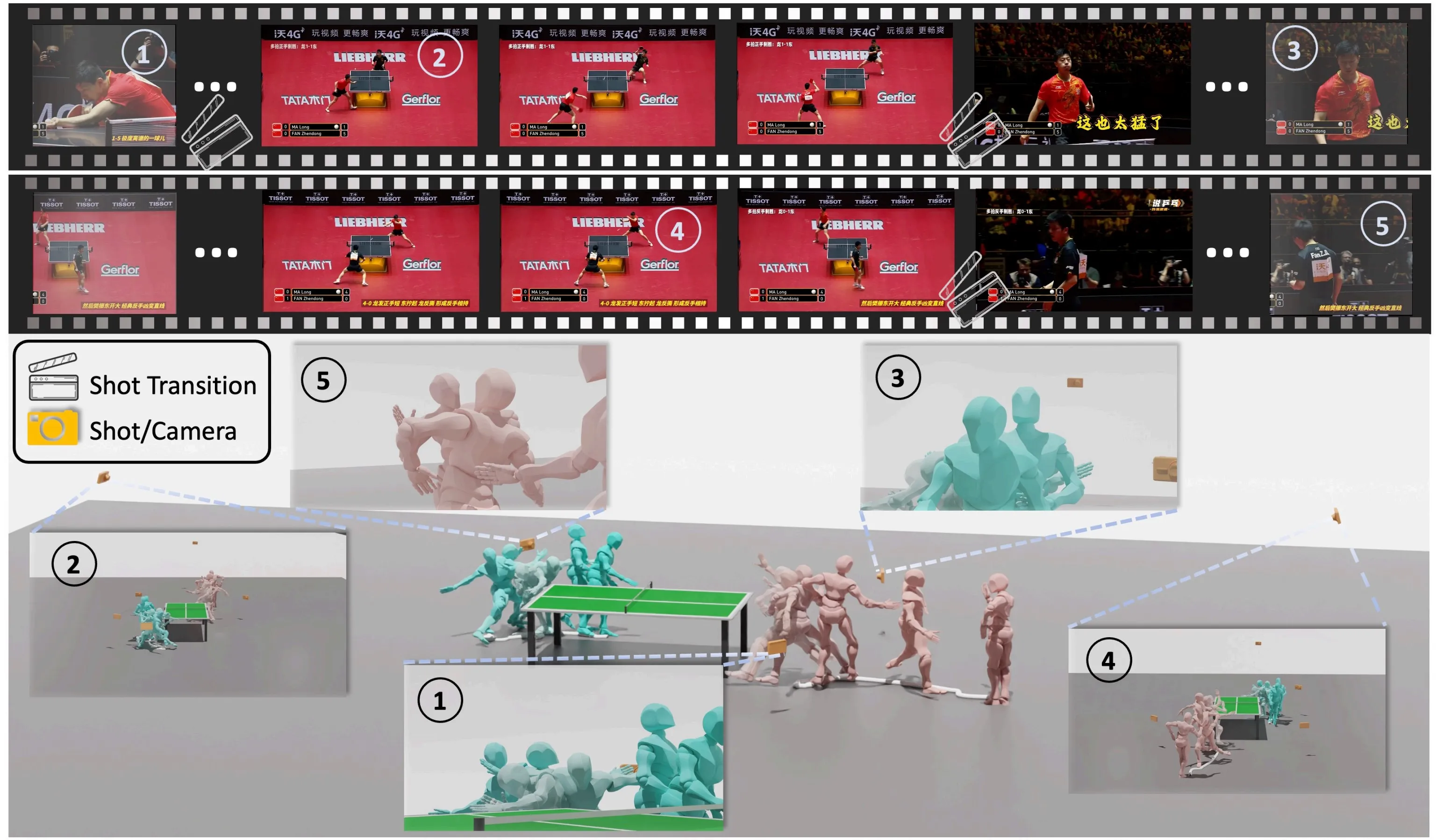
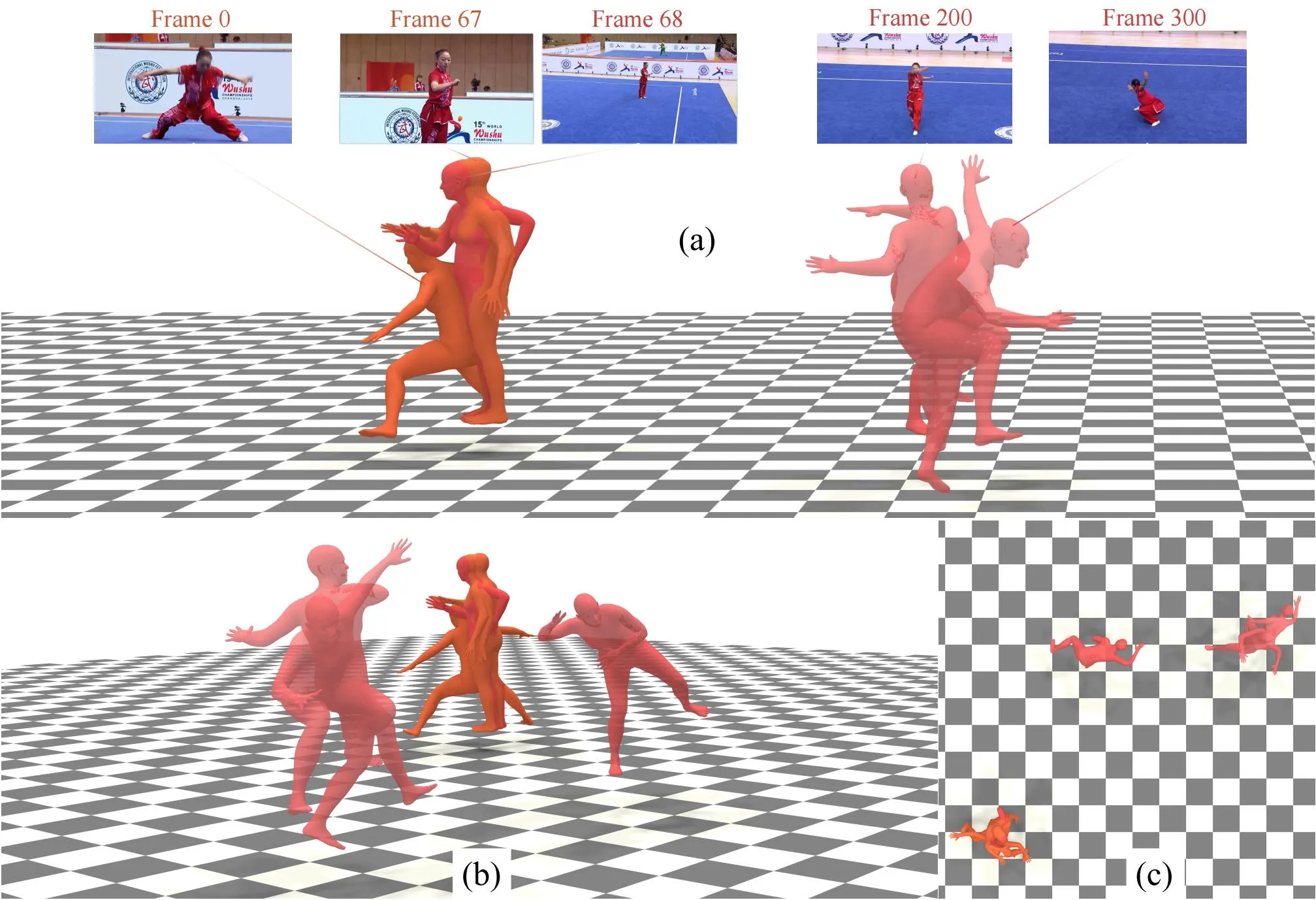
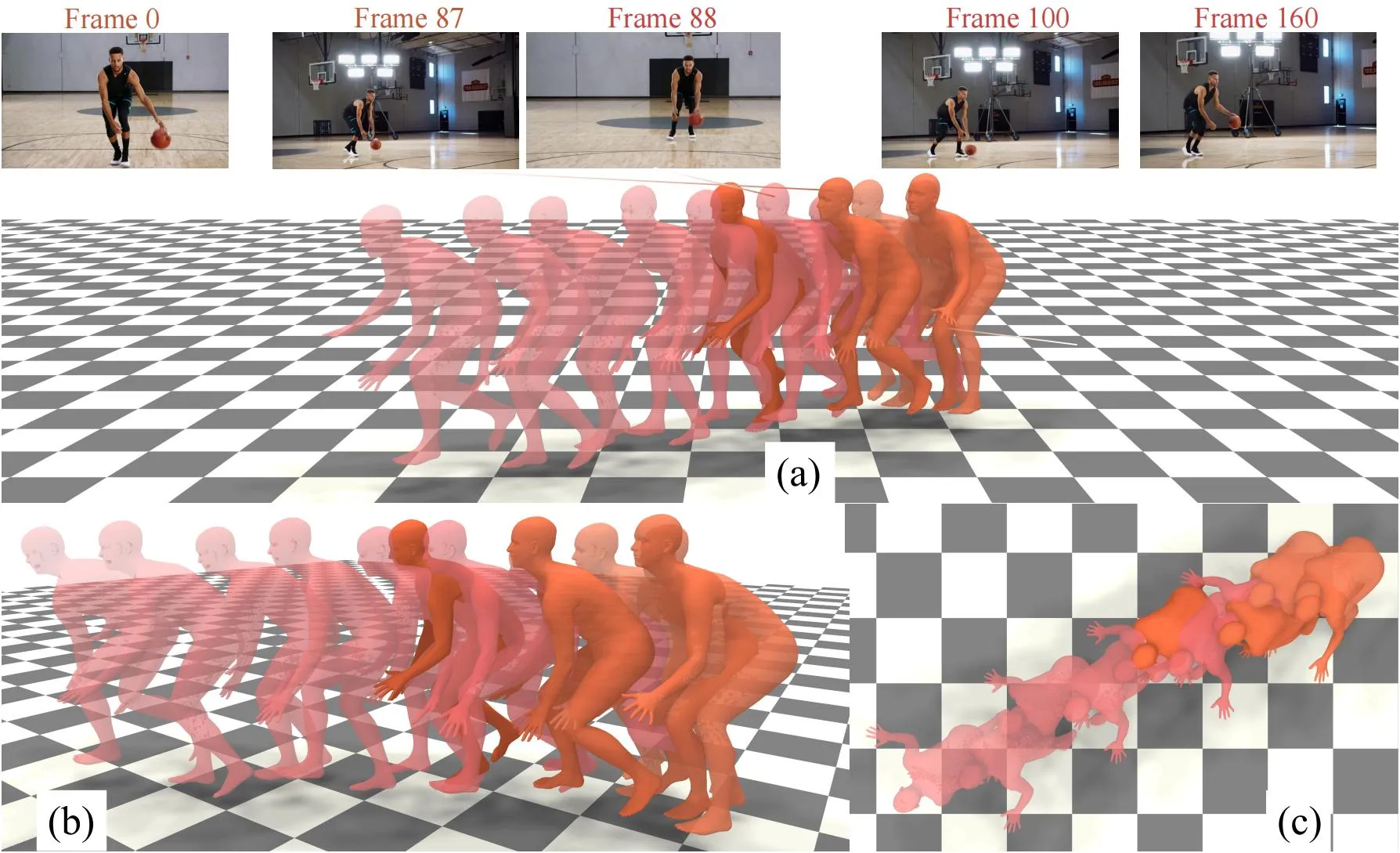
we present a novel framework designed to reconstruct long-sequence 3D human motion in the world coordinates from in-the-wild videos with multiple shot transitions. Such long-sequence in-the-wild motions are highly valuable to applications such as motion generation and motion understanding, but are of great challenge to be recovered due to abrupt shot transitions, partial occlusions, and dynamic backgrounds presented in such videos. Existing methods primarily focus on single-shot videos, where continuity is maintained within a single camera view, or simplify multi-shot alignment in camera space only. In this work, we tackle the challenges by integrating an enhanced camera pose estimation with Human Motion Recovery (HMR) by incorporating a shot transition detector and a robust alignment module for accurate pose and orientation continuity across shots. By leveraging a custom motion integrator, we effectively mitigate the problem of foot sliding and ensure temporal consistency in human pose. Extensive evaluations on our created multi-shot dataset from public 3D human datasets demonstrate the robustness of our method in reconstructing realistic human motion in world coordinates.
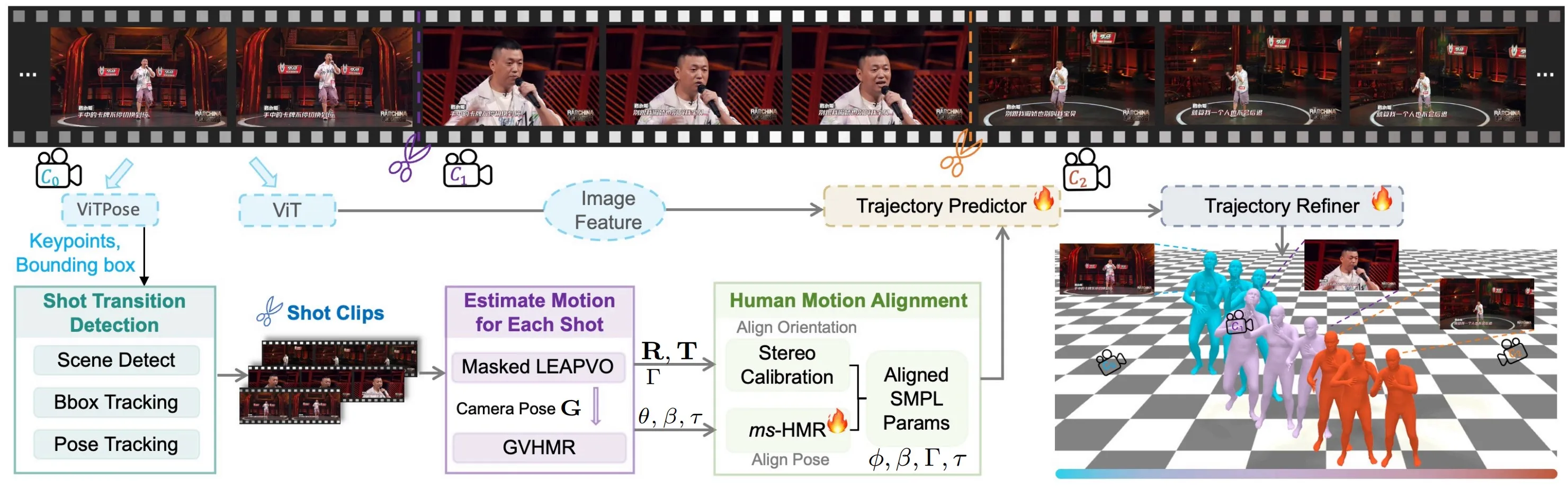
HumanMM processes multi-shot video sequences by first extracting motion feature such as keypoints and bounding boxes, using ViTPose and image feature using ViT. These features are then segmented into single-shot clips via Shot Transition Detection (Sec. 3.2). Initialized camera (camera rotation R and camera translation T) and human (SMPL) parameters for each shot are estimated using Masked LEAP-VO (Sec. 3.3) and GVHMR. Human orientation is aligned across shots through camera calibration (3.4.1), and ms-HMR (Sec. 3.4.2) ensures consistent pose alignment. Finally, a bi-directional LSTM-based trajectory predictor with trajectory refiner predicts trajectory based on aligned motion and mitigates foot sliding throughout the video.
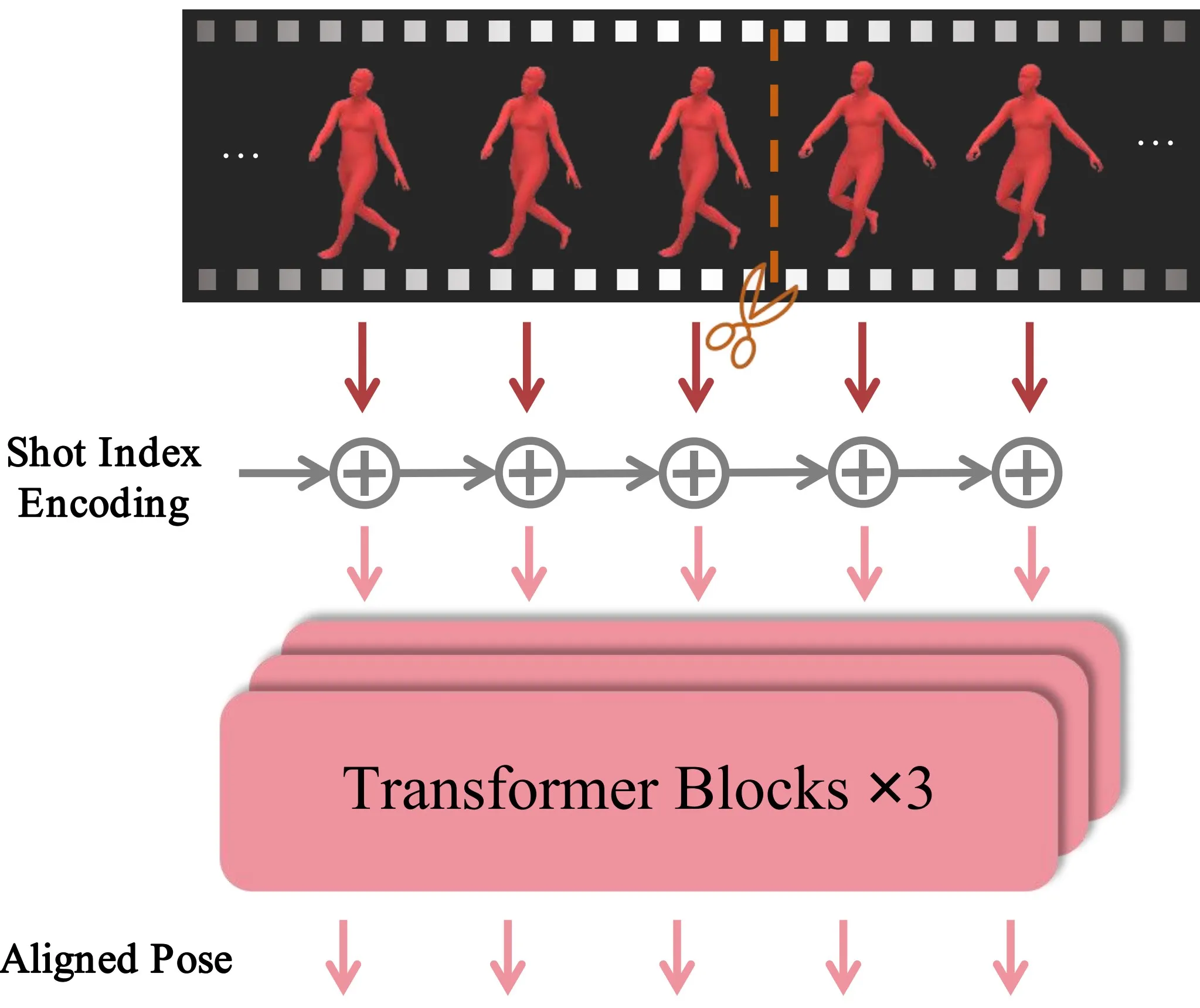
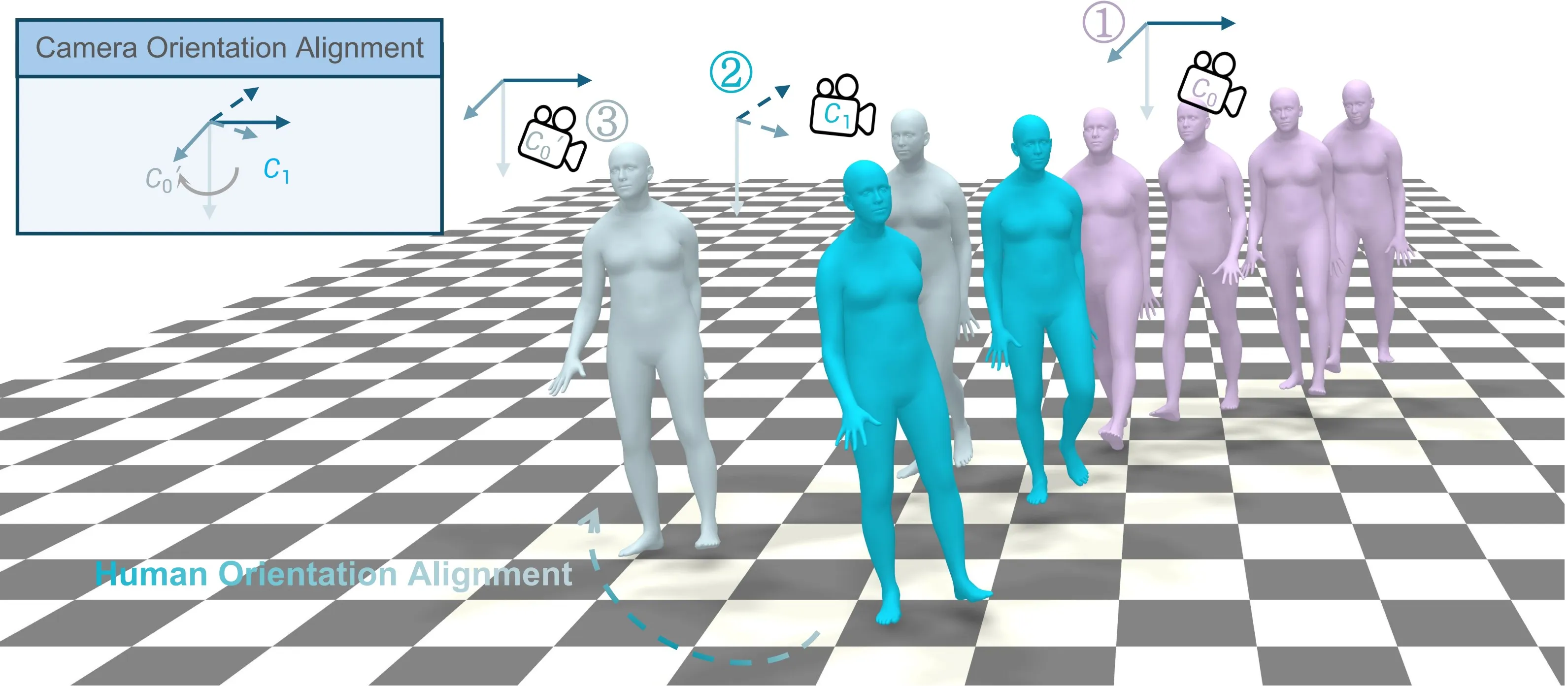
To align the orientations between two frames with shot transition, we decompose the human orientation with shot transitions in world coordinates as,
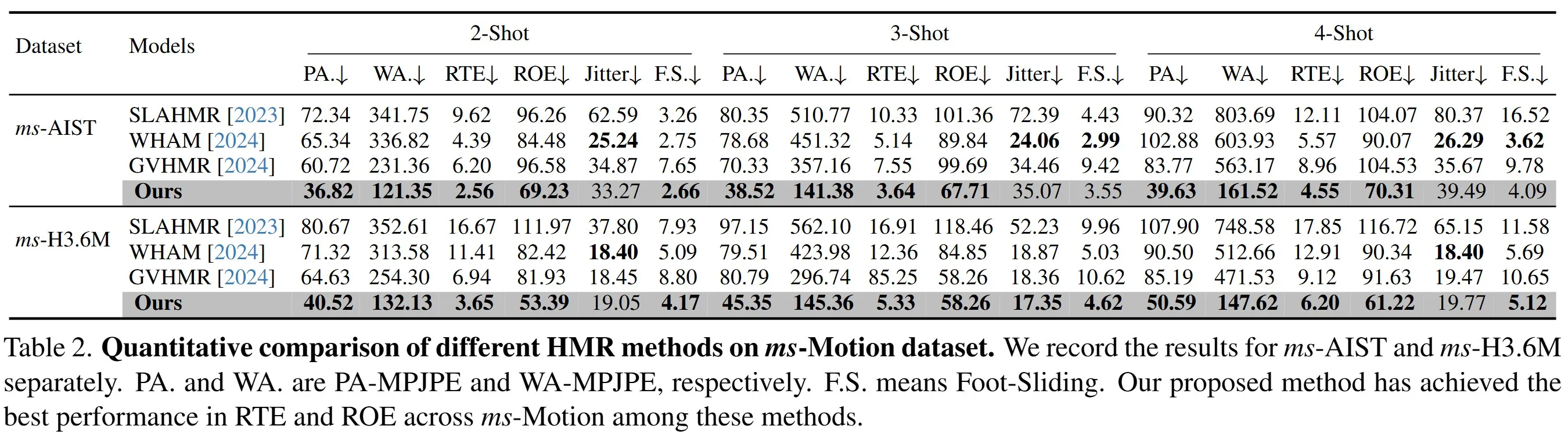
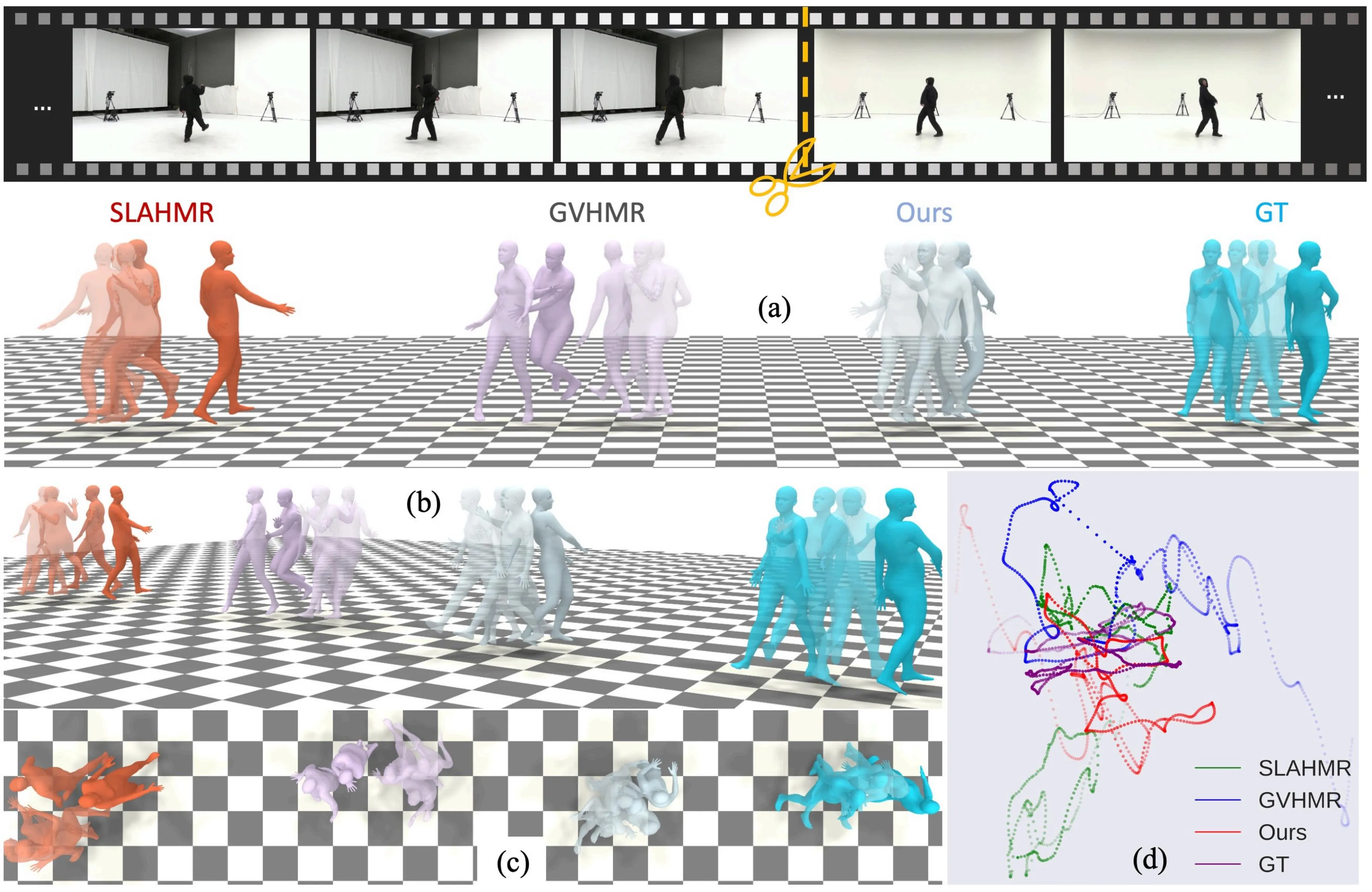
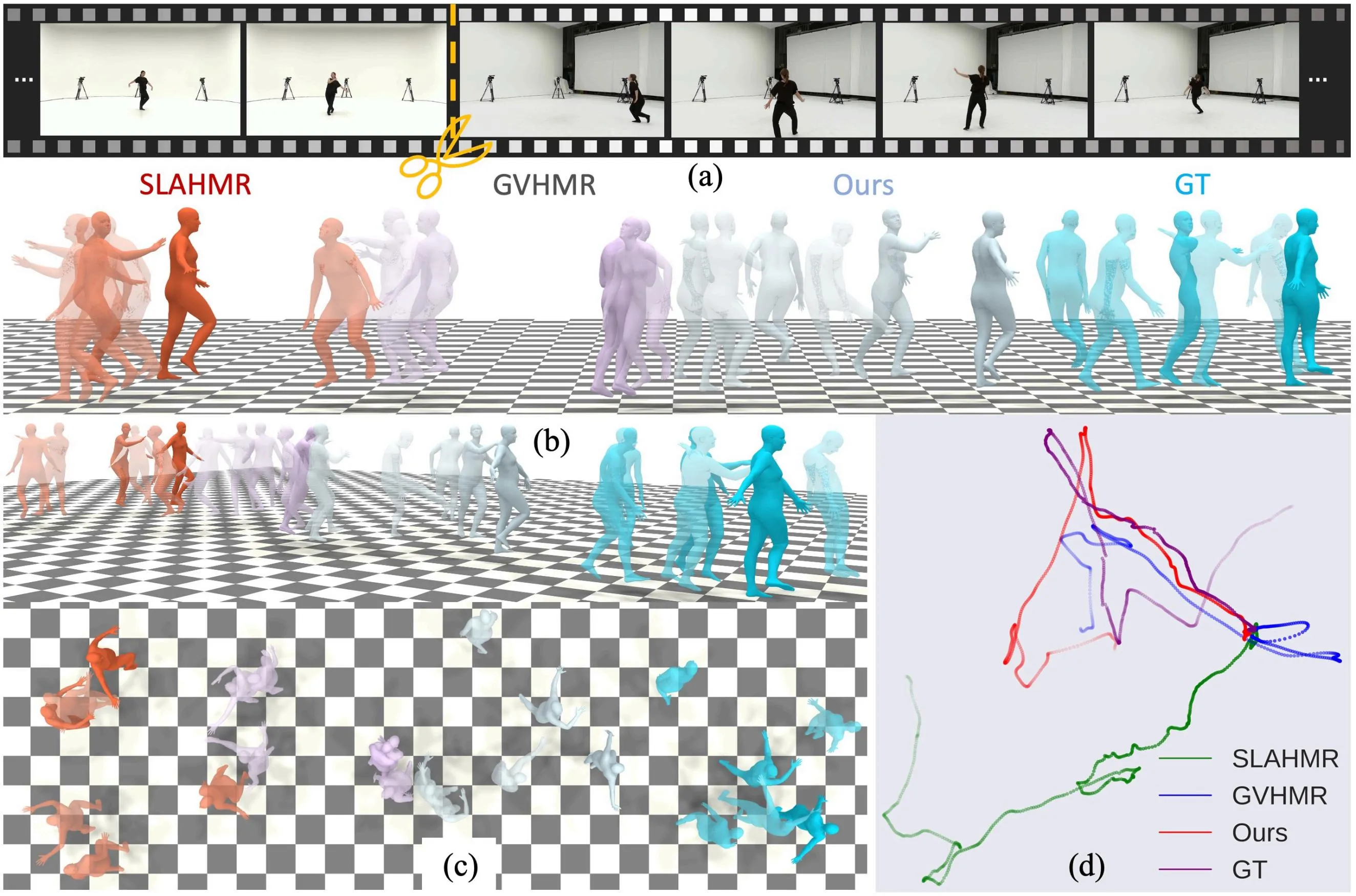
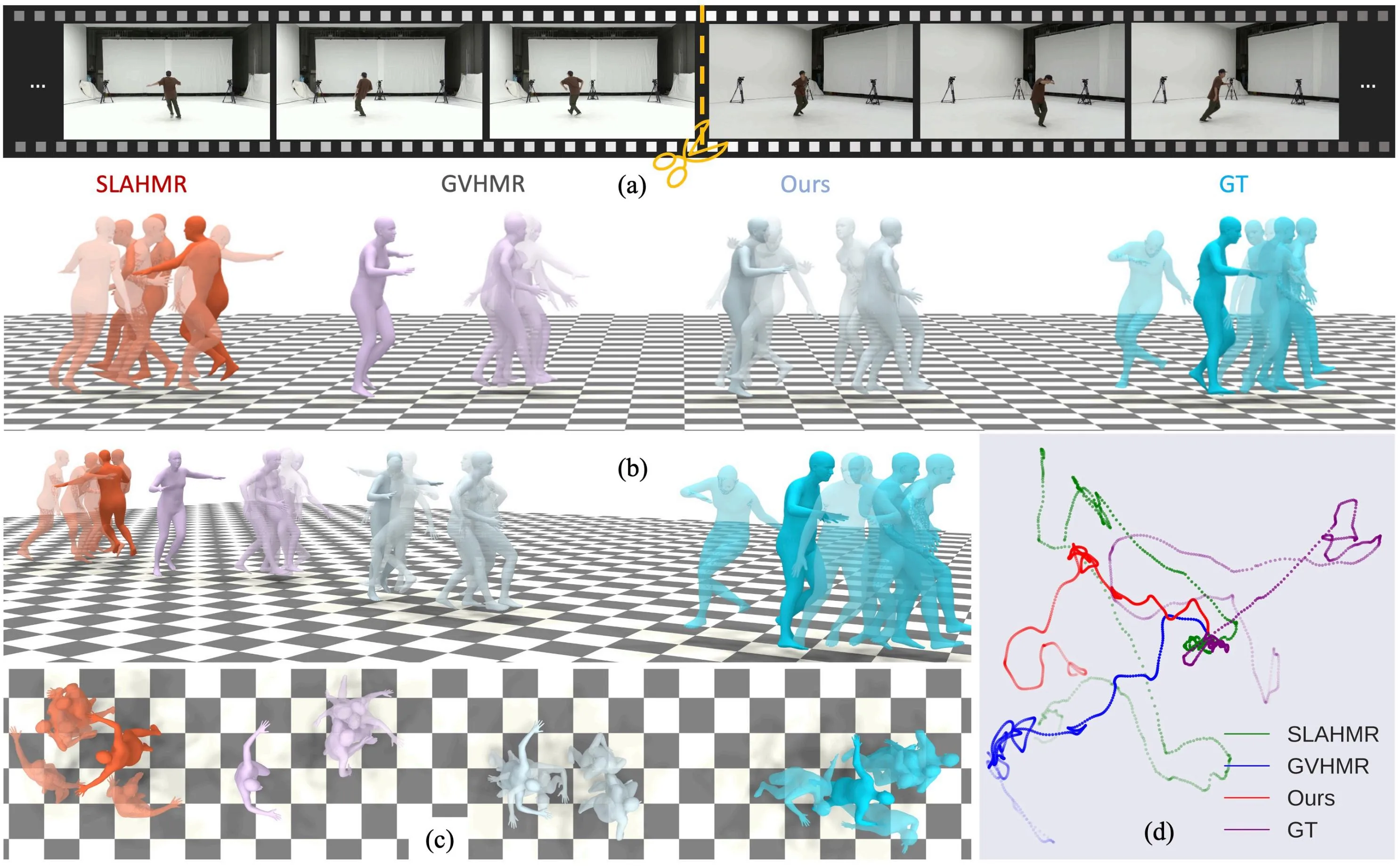
We compare our proposed method with several state-of-the-art HMR methods SLAHMR, WHAM and GVHMR on our proposed benchmark. As illustrated in the table below, our proposed method has achieved the best performance for PA&WA-MPJPE, RTE and ROE through videos with all numbers of shots across msaist and msh36m, indicating that our method reconstructs both the global human motion and orientations in the world coordinates more accurately and robustly. For the foot sliding metric, our method also performs as the best across all numbers of shots.
This work was partially funded by the Shen-zhen Science and Technology Project under Grant KJZD20240903103210014. Work done by Yuhong Zhang, Guanlin Wu, Ling-Hao Chen, Jing Lin and Jiamin Wu during the internship at IDEA Research. The author team would also like to convey sincere thanks to Ms. Yaxin Chen from IDEA Research for the expressive dance motion used in the demo presentation.
@misc{zhang2025humanmmglobalhumanmotion,
title={HumanMM: Global Human Motion Recovery from Multi-shot Videos},
author={Yuhong Zhang and Guanlin Wu and Ling-Hao Chen and Zhuokai Zhao and Jing Lin and Xiaoke Jiang and Jiamin Wu and Zhuoheng Li and Hao Frank Yang and Haoqian Wang and Lei Zhang},
year={2025},
eprint={2503.07597},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.07597},
}